Published: August 12, 2024 | Updated: October 09, 2025
Published: August 12, 2024 | Updated: October 09, 2025
Strategic Maintenance Scheduling for Better Operations
 Scheduled maintenance programs create a structured approach to asset care and reliability. These programs depend on timed intervals or condition-based triggers to initiate repairs and inspections. In industries where machinery and systems must perform without interruption, scheduled maintenance offers a valuable solution. This article looks at strategic maintenance scheduling for better operations and the use of digital tools like a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
Scheduled maintenance programs create a structured approach to asset care and reliability. These programs depend on timed intervals or condition-based triggers to initiate repairs and inspections. In industries where machinery and systems must perform without interruption, scheduled maintenance offers a valuable solution. This article looks at strategic maintenance scheduling for better operations and the use of digital tools like a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
Understanding the Role of Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance includes tasks that must happen at predetermined times to ensure smooth operations. Whether performed weekly, monthly, or annually, these activities maintain asset reliability and prevent costly failures. The strategy outlines not just what gets done, but also when, where, and by whom. It involves aligning maintenance needs with available workforce capacity, resource availability, and the asset’s operational importance.
While sometimes confused with planned maintenance, scheduled maintenance plays a more time-sensitive role. Planning prepares the resources, tools, and procedures. Scheduling applies these plans to a calendar or timetable and assigns the work to specific individuals or teams. These efforts work best when done in concert, as successful outcomes depend on both accurate preparation and timely execution. For a complete discussion of both, read the book by Doc Palmer.
From Work Requests to Work Orders
Each scheduled maintenance event begins with a clear trigger. This can take the form of a work request generated during routine inspections or based on manufacturer recommendations. Once reviewed, a supervisor approves the request. A planner identifies the necessary materials, while a scheduler determines the ideal time slot. From there, a work order gets issued, detailing the scope of work and responsibilities.
Assigning the job requires attention to both technical needs and human availability. The right technician must have access to the right tools, all within the right window of time. Misalignments in these areas delay repairs, increase costs, or cause workflow interruptions. Successful scheduling reduces these risks by integrating job estimates, labor hours, and asset access.
An Example from the Field
Imagine a manufacturing facility operating with precision equipment across multiple production lines. Technicians perform inspections and alignments at regular intervals. In one case, a specialist notes an unusual vibration pattern in a motor. Rather than reacting to a full breakdown later, a work order gets submitted. After evaluation, the scheduler books the repair during an off-shift window, avoiding disruption.
This preemptive action avoids unscheduled downtime and protects production targets. A minor component gets replaced, and the machine resumes standard operation. The only way this repair happens so efficiently is due to clear scheduling and defined responsibilities.
Benefits of Effective Scheduled Maintenance
1. Fewer Unexpected Failures
Early detection of minor wear or system imbalance reduces the risk of full breakdowns. Regular maintenance checks catch problems before they grow, saving time and resources. This lowers the frequency of emergency repairs and supports more predictable operations.
2. Higher Workforce Efficiency
Technicians work smarter when schedules eliminate guesswork. Clear instructions and accurate timing increase the number of tasks completed in a shift. Unplanned delays decrease, allowing teams to maintain focus and pace. Productivity rises as coordination improves.
3. Extended Equipment Lifespan
Routine service maintains mechanical health. Bearings stay lubricated, electrical systems stay calibrated, and moving parts resist fatigue. This attention to detail delays the need for expensive replacements. Long-term savings result from fewer capital expenditures on new machinery.
4. Lower Operational Costs
When systems run efficiently and avoid emergency interventions, operational costs drop. Scheduled repairs typically cost less than reactive repairs due to reduced overtime, expedited shipping, or secondary damage. Fewer breakdowns also protect productivity and revenue.
5. Improved Safety and Liability Management
Well-maintained equipment lowers the risk of accidents. Compliance inspections pass more smoothly. Insurance risks decrease, and the workplace fosters confidence in its safety standards. These advantages matter for both staff morale and regulatory standing.
How CMMS Enhances Scheduling Success
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) introduces structure and accessibility to maintenance workflows. It centralizes asset records, tracks inventory levels, and stores all work history. Users can assign jobs, set reminders, and evaluate performance—all within a single platform.
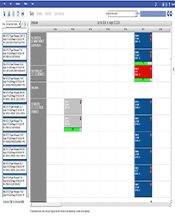
One feature that supports scheduling directly is the digital calendar interface. With drag-and-drop functionality, users assign work orders visually. This visibility allows scheduling over days, weeks, or even months in advance. Conflicts and overlaps become easy to identify and correct.
In real time, supervisors check status updates, labor allocation, and task completion rates. These insights support quick adjustments when unexpected events occur. Over time, data collected by a CMMS shapes better decisions. It identifies asset trends, technician performance, and workload balance.
Discover how streamlined maintenance processes can elevate production. Learn more.
Keys to Sustained Improvement
Success in scheduled maintenance stems from consistent application of its principles. Every task needs thoughtful planning, and every work order must include clear deadlines. Teams succeed when expectations align with available skills, tools, and timeframes.
Leadership plays a central role in setting the tone for scheduled maintenance culture. When expectations are clear and the workforce has the tools and training to meet them, performance follows. Communication across departments ensures visibility into timelines and priorities. As accountability grows, so does the quality of asset care.
Digital solutions, such as CMMS platforms, help scale this structure. They reduce administrative delays and support more accurate reporting. When paired with trained teams and supportive supervisors, digital scheduling systems enhance the overall reliability of maintenance programs.
Building Reliability Through Scheduled Maintenance
Consistency, preparation, and good judgment form the foundation of any successful maintenance program. Scheduled maintenance gives organizations a methodical way to stay ahead of failure and maintain reliability. It's not about working harder—it's about planning smarter and acting at the right time.
FAQs
What is scheduled maintenance and why is it important?
Scheduled maintenance involves performing tasks at predetermined intervals to ensure equipment reliability and prevent costly failures.
How does a CMMS improve maintenance scheduling?
A CMMS centralizes work orders, tracks inventory, and provides a digital calendar for efficient job assignment and timeline management.
What are the benefits of implementing a maintenance schedule?
Benefits include fewer unexpected failures, higher workforce efficiency, extended equipment lifespan, lower operational costs, and improved safety.
How can MAPCON’s CMMS help prevent downtime?
MAPCON’s CMMS allows real-time tracking of work orders and proactive scheduling, reducing unscheduled downtime and keeping production on target.
What’s the difference between planned and scheduled maintenance?
Planned maintenance prepares resources and procedures, while scheduled maintenance applies those plans to specific times and assigns tasks to teams.
How does strategic scheduling improve workforce productivity?
Clear schedules and defined responsibilities help technicians work efficiently, reducing delays and increasing the number of tasks completed per shift.
MAPCON | 800-922-4336
MAPCON CMMS software empowers you to plan and execute PM tasks flawlessly, thanks to its wealth of features and customizable options. Want to see it for yourself? Click the button below to get your FREE 30-day trial of MAPCON!
Try It FREE!